While the exact number of medics who died in Iraq is unclear, dozens of combat medics and corpsmen from the U.S. military lost their lives, often while saving others in active combat zones.
In this article, we’ll explore how many medics died in Iraq, the vital role they played during the war, and the lasting legacy of their heroism.
Who Were the Medics in Iraq?
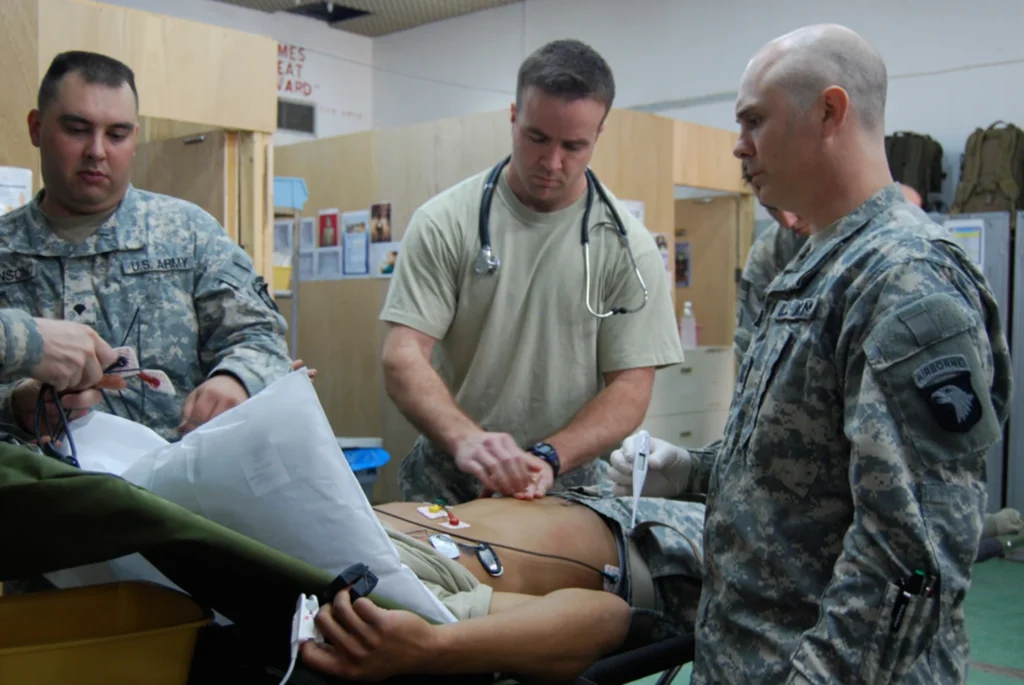
Medics are healthcare professionals trained to provide emergency care in combat zones. In Iraq, medics served in various roles across all branches of the military:
- Combat Medics: Assigned directly to infantry units, they operated on the front lines, stabilizing injured soldiers and preparing them for evacuation.
- Flight Medics: Provided medical care in helicopters, often under fire, during rapid evacuations.
- Navy Corpsmen: Worked with Marine units, offering immediate care during missions.
- Field Hospital Personnel: Delivered advanced medical care in makeshift hospitals near combat zones.
Medics in Iraq faced unique challenges, including urban warfare, improvised explosive devices (IEDs), and limited access to advanced medical resources. They worked tirelessly to save lives, often putting themselves in harm’s way.
How Many Medics Died in Iraq?
While the exact number of medics who died in Iraq is difficult to pinpoint, estimates suggest that dozens of combat medics and corpsmen lost their lives during the conflict. This figure includes medics from the U.S. Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps.
Many medics died while attending to wounded soldiers in active combat zones. IEDs, sniper attacks, and ambushes were common causes of death. Their willingness to step into danger to save others exemplifies the selflessness and bravery that defines the role of a medic.
Challenges Faced by Medics in Iraq:
Medics in Iraq faced a range of challenges that tested their resilience and skills:
Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs):
- IEDs were responsible for a significant portion of injuries and fatalities in Iraq. Medics were often the first to respond to these devastating attacks, putting themselves at risk of secondary explosions.
Urban Warfare:
- Battles in cities like Fallujah and Baghdad meant operating in close quarters with limited visibility and high danger. Medics worked under intense conditions, often treating multiple casualties simultaneously.
Limited Resources:
- Medics frequently had to improvise treatments due to a lack of advanced medical supplies in combat zones. Quick thinking and adaptability were essential to saving lives.
Emotional Toll:
- Witnessing severe injuries and losing fellow soldiers took a significant emotional toll on medics. Many carried the psychological scars of war long after returning home.
Also Read: Can A Married Couple Apply For Medical Seperately – Separate Medical Applications for Couples!
Notable Stories of Fallen Medics:
While every medic’s story is worth honoring, some individuals stand out for their extraordinary courage:
Army Specialist Christopher G. Scherer:(1983–2007)
Scherer was a combat medic who lost his life while serving in Al Anbar Province. He was remembered for his unwavering dedication to his unit and his efforts to provide medical care even under heavy fire.
Navy Corpsman HM3 Christopher Anderson:(1980–2006)
Serving alongside Marine units, Anderson was killed in action while attending to wounded Marines during a firefight. His bravery exemplified the selflessness of Navy corpsmen.
Sergeant First Class Jared C. Monti:(1975–2006)
Though not a medic, Monti’s actions highlight the dangers medics often faced. He repeatedly exposed himself to enemy fire to save his comrades, a commitment shared by many medics in the field.
How Medics Saved Lives in Iraq?
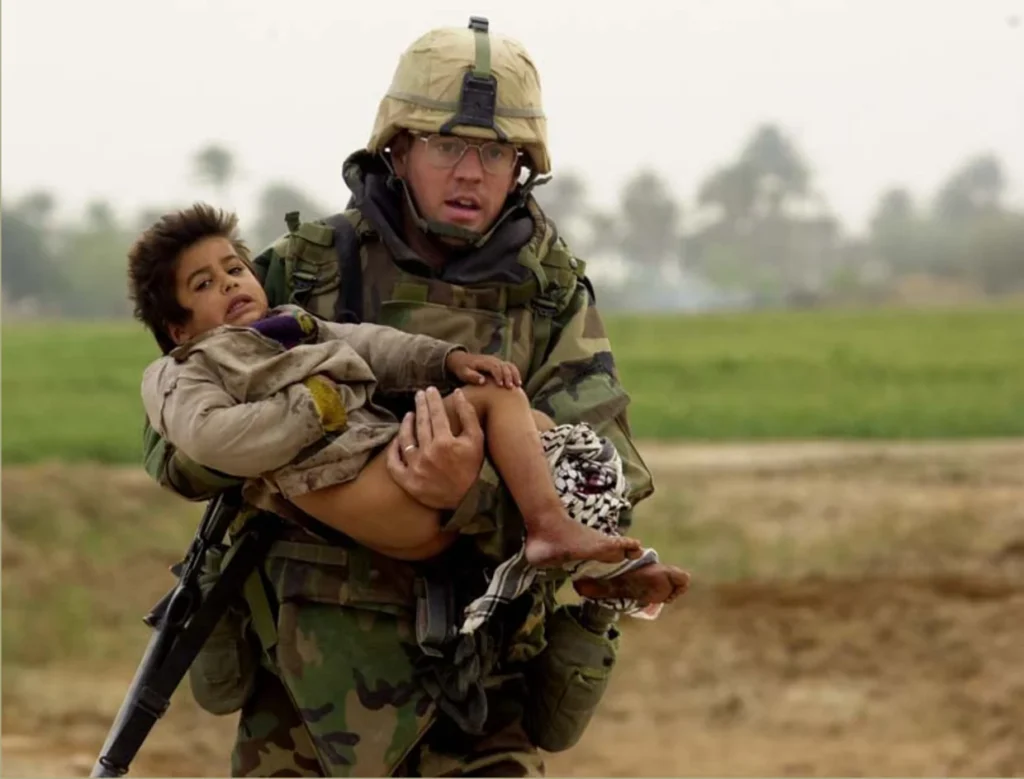

Despite the dangers, medics in Iraq played a pivotal role in reducing battlefield fatalities. Their immediate care often made the difference between life and death. Key contributions include:
- Rapid Response: Medics were trained to stabilize patients within the critical “golden hour,” increasing survival rates.
- Evacuation Support: Working with flight medics, they ensured injured personnel reached medical facilities quickly.
- Training Fellow Soldiers: Medics often trained other soldiers in basic first aid, ensuring lifesaving skills were distributed across units.
The Legacy of Medics in Iraq:
The contributions of medics in Iraq extend far beyond the battlefield. Their experiences have influenced military medicine and emergency care protocols, improving treatment for soldiers in future conflicts. Key legacies include:
Advancements in Trauma Care:
- Techniques pioneered in Iraq, such as the use of tourniquets and hemostatic agents, are now standard in both military and civilian trauma care.
Mental Health Awareness:
- The emotional toll on medics has highlighted the need for comprehensive mental health support for military personnel.
Inspiration for Future Generations:
- The courage of medics who served in Iraq continues to inspire new recruits and medical professionals.
Honoring Their Sacrifice:
The sacrifices of medics in Iraq are commemorated through various memorials and tributes:
- The Wall of Heroes: Many fallen medics’ names are inscribed on national and military memorials.
- Posthumous Awards: Medics who displayed extraordinary bravery received honors such as the Silver Star, Bronze Star, and Purple Heart.
- Veterans’ Stories: Organizations and veterans’ groups work to preserve the stories of medics, ensuring their contributions are never forgotten.
FAQ’s
1. How many medics died in Iraq?
While the exact number is unclear, dozens of U.S. military medics and corpsmen lost their lives during the conflict, many while saving others.
2. What were the main causes of medic deaths in Iraq?
IEDs, sniper attacks, and ambushes were common causes of death for medics in Iraq.
3. What challenges did medics face in Iraq?
Medics faced challenges like IEDs, urban warfare, limited medical supplies, and emotional trauma.
4. Did medics receive recognition for their service?
Yes, many medics received posthumous honors, including the Silver Star, Bronze Star, and Purple Heart.
5. How did medics save lives in Iraq?
Medics stabilized soldiers during the critical “golden hour,” coordinated evacuations, and trained others in first aid.
Conclusion
Medics who served in Iraq were more than just healthcare providers—they were lifelines for their comrades, often risking their lives to save others. The dozens of medics who died in Iraq remind us of the immense sacrifices made by military personnel in the line of duty.
As we remember their contributions, we honor their legacy and the vital role medics continue to play in ensuring the safety and well-being of soldiers on the front lines. Their courage and selflessness will forever remain an inspiration.

Leave a Reply