Bariatric patients are at higher risk for dental inflammation due to nutritional deficiencies and reduced saliva. Management includes antibiotics, topical treatments, and preventive care.
This article delves into the connection between bariatric surgery and dental inflammation, exploring the causes, symptoms, effective medications, and preventive measures to help patients maintain optimal oral health.
Understanding Dental Inflammation in Bariatric Patients:

What Is Dental Inflammation?
Dental inflammation typically refers to conditions like gingivitis and periodontitis, where the gums become inflamed due to the presence of harmful bacteria and plaque. In bariatric patients, the incidence of dental inflammation can increase for various reasons:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Following surgery, patients often experience restrictions in their diet, which can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals. Key nutrients such as vitamin C (crucial for collagen production and gum health) and calcium (important for teeth and bone strength) may become scarce. This nutritional deficit weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections and inflammation.
- Altered Oral Microbiome: Bariatric surgery can change the composition of the oral microbiome. A balanced microbiome is essential for maintaining oral health, and an imbalance can lead to increased bacterial growth that contributes to gum disease and inflammation.
- Increased Bacterial Growth: Some post-surgical dietary changes may lead to higher consumption of sugary or acidic foods, which can contribute to tooth decay and inflammation. Foods that are high in sugar can create an environment conducive to the proliferation of harmful bacteria in the mouth.
- Reduced Saliva Production: Bariatric surgery can affect saliva production, which plays a crucial role in oral health. Saliva helps neutralize acids produced by bacteria, washes away food particles, and provides essential minerals to teeth. A reduction in saliva can increase the risk of dental decay and inflammation.
The Connection Between Obesity, Bariatric Surgery, and Oral Health:
Obesity itself is a known risk factor for periodontal disease, leading to systemic inflammation and a compromised immune response. After undergoing bariatric surgery, patients may experience rapid weight loss, which can also trigger hormonal changes that further influence oral health.
Psychological Aspects:
Moreover, the psychological impact of bariatric surgery can lead to changes in eating behavior and emotional health, which may also affect oral hygiene practices. Increased stress and emotional eating can sometimes lead to poor dietary choices, further exacerbating oral health issues.
Recognizing Symptoms of Dental Inflammation:
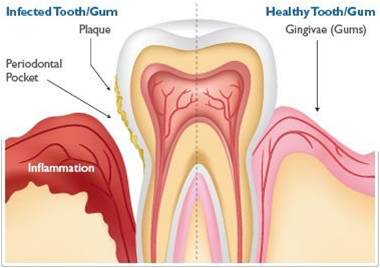
Bariatric patients must be proactive in monitoring their dental health. Recognizing the signs of dental inflammation early can prevent more severe complications. Key symptoms include:
- Red, Swollen, or Bleeding Gums: One of the first indicators of gum disease, often noticed while brushing or flossing.
- Persistent Bad Breath: A common symptom of gum disease caused by bacterial buildup.
- Pain or Discomfort While Chewing: Sensitivity or pain in the gums can indicate inflammation.
- Receding Gums: Gums may begin to pull away from teeth, exposing more of the tooth surface and increasing sensitivity.
- Loose Teeth: Advanced periodontal disease can cause teeth to loosen as the supporting bone structure deteriorates.
If any of these symptoms occur, consulting a dental professional promptly is crucial.
Medications for Managing Dental Inflammation:
Managing dental inflammation in bariatric patients often requires a comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle adjustments and medications. Here are some commonly prescribed medications and treatments:
Antibiotics:
In severe cases of dental inflammation, antibiotics may be necessary to combat bacterial infections. Dentists may prescribe:
- Amoxicillin: Frequently used to treat various bacterial infections, including those affecting the gums.
- Clindamycin: An effective alternative for patients with a penicillin allergy, it targets anaerobic bacteria that commonly contribute to periodontal disease.
Topical Treatments:
Topical treatments can effectively reduce inflammation and promote healing in the gums. Options include:
- Chlorhexidine Gluconate: This antiseptic mouthwash is often recommended to reduce bacteria and plaque in the mouth, particularly after dental procedures.
- Fluoride Gel: This treatment can help strengthen enamel, particularly for patients at risk of dental decay due to dietary changes.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in the gums. Common options include:
- Ibuprofen: Often used for its pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Naproxen: Another effective NSAID for managing pain and inflammation.
Pain Relievers:
Alongside NSAIDs, other pain relievers may be recommended based on the severity of discomfort. These medications can provide relief while other treatments address the underlying inflammation.
Nutritional Supplements:
While not medications, nutritional supplements can be crucial in preventing deficiencies that contribute to dental inflammation. Bariatric patients should consider:
- Multivitamins: These can help ensure adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Important for maintaining bone health, including the jawbone that supports teeth.
Preventing Dental Inflammation Post-Bariatric Surgery:
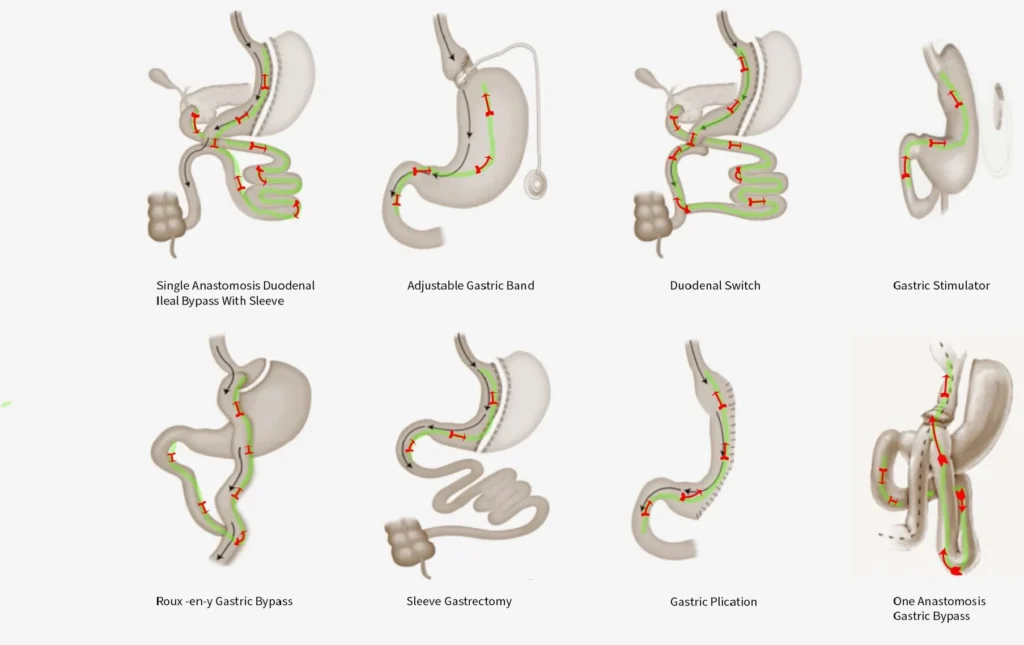
Preventive measures are crucial for maintaining oral health after bariatric surgery.”Here are a few strategies to keep in mind”
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Routine dental visits can help identify and address potential issues early. Dentists can provide professional cleanings and personalized advice tailored to the needs of bariatric patients.
- Good Oral Hygiene Practices: Establishing a diligent oral hygiene routine is essential. Brush your teeth at least twice daily using fluoride toothpaste, and floss each day to eliminate food particles.particles and plaque from between teeth, and consider using an antiseptic mouthwash to help reduce bacteria.
- Balanced Diet: Emphasize a nutritious diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean sources of protein. Limit sugary and acidic foods that can exacerbate dental issues. Incorporating foods high in vitamins A and C can promote gum health.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining saliva production, which plays a vital role in oral health. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day to help keep the mouth moist.
- Smoking Cessation: If applicable, quitting smoking can improve oral health and reduce inflammation. Tobacco use is strongly linked to gum disease and can significantly impair healing.
- Education on Oral Health: Bariatric patients should receive education about the importance of oral health post-surgery. Understanding the connection between diet, oral hygiene, and dental health can empower patients to make better choices.
- Utilizing Dental Products: Use dental products designed for sensitive gums and teeth. Products like toothpaste specifically formulated for gum health can aid in reducing inflammation and discomfort.
Collaborating with Healthcare Professionals:
A collaborative approach involving both dental and medical professionals can help manage and prevent dental inflammation in bariatric patients. Patients should communicate openly with their healthcare providers about any oral health concerns, dietary habits, and changes in their health status post-surgery.
Team Approach to Care:
- Dietitians: Working with a registered dietitian can help bariatric patients develop a balanced meal plan that meets their nutritional needs while promoting oral health.
- Dentists: Regular visits to the dentist for cleanings and check-ups are crucial. Dentists can monitor oral health, provide professional cleanings, and recommend personalized oral hygiene practices.
- Medical Doctors: Coordinating care with primary healthcare providers can ensure that any systemic health issues are addressed, which can impact oral health.
FAQ’s
- What is dental inflammation in bariatric patients?
Dental inflammation includes conditions like gingivitis and periodontitis, caused by bacteria and plaque buildup, often exacerbated by nutritional deficiencies after surgery.
- What are common symptoms of dental inflammation?
Symptoms include swollen or bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, gum pain, receding gums, and loose teeth.
- What medications are recommended for managing dental inflammation?
Treatment may include antibiotics (like amoxicillin), topical treatments (like chlorhexidine gluconate), and anti-inflammatory medications (like ibuprofen).
- How can dental inflammation be prevented after bariatric surgery?
Preventive measures include regular dental check-ups, maintaining good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and following a balanced diet.
- Why is dental health important for bariatric patients?
Proper dental health prevents complications, ensures better overall health, and supports the success of bariatric surgery by allowing patients to maintain good nutrition.
Conclusion
Bariatric patients face unique challenges regarding dental health, particularly concerning inflammation. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing symptoms early, and seeking appropriate medication can help manage and prevent these issues. By prioritizing good oral hygiene, maintaining a balanced diet, and working closely with healthcare professionals, bariatric patients can enjoy better overall health and a brighter smile.
Leave a Reply