Medications like fluoroquinolones, corticosteroids, tamoxifen, epinephrine eye drops, and thiazolidinediones can increase the risk of retinal detachment.
In this article, we’ll explore which medications can lead to retinal detachment and why it’s important to be aware of these risks.
Medications Linked to Retinal Detachment:
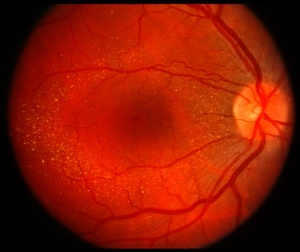
Some medications may contribute to retinal detachment, either by directly affecting the retina or by increasing susceptibility to conditions that lead to detachment. Here are the most commonly implicated drugs:
Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics:
- Examples: Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin
- These antibiotics are widely used for bacterial infections. Studies suggest they may increase the risk of retinal detachment, possibly by weakening the vitreous gel inside the eye.
Corticosteroids:
- Examples: Prednisone, Dexamethasone
- Used to treat inflammation and autoimmune conditions, corticosteroids can lead to complications such as posterior vitreous detachment (PVD), which might precede retinal detachment.
Tamoxifen:
- A drug commonly prescribed for breast cancer, Tamoxifen has been linked to retinal toxicity and the formation of deposits in the retina, increasing the risk of detachment.
Epinephrine-Based Medications:
- Found in some eye drops for glaucoma, these medications can sometimes lead to complications, including retinal detachment, particularly in susceptible individuals.
Also Read: Ketamine as a Treatment for Depression
Thiazolidinediones :(TZDs)
- Examples: Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone
- Used for type 2 diabetes, these medications may contribute to fluid buildup in the eye, leading to conditions like macular edema, which can predispose the retina to detachment.
Factors That Amplify Risk:
While these medications can pose risks, other factors often contribute to the likelihood of retinal detachment:
- High Myopia: People with severe nearsightedness have thinner retinas, making them more vulnerable.
- Eye Surgeries: Procedures like cataract surgery can increase susceptibility.
- Trauma: Any injury to the eye can destabilize the retina.
- Age: Retinal detachment becomes more common as you age.
Recognizing the Symptoms:

Early detection is crucial. Symptoms of retinal detachment include:
- Sudden appearance of floaters or flashes of light
- A shadow or curtain over part of your vision
- Blurred or distorted vision
If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
How to Protect Your Eyes?
Regular Eye Exams:
Routine eye check-ups are essential for detecting early signs of retinal issues, including potential detachment. Regular exams allow your eye doctor to monitor the health of your eyes, identify any risk factors, and catch problems before they worsen. Early detection can lead to prompt treatment, helping to prevent more severe complications and preserve your vision.
Eye exams may include tests like retinal imaging or dilation, which help in spotting abnormalities that may not be visible otherwise. By keeping up with these visits, you ensure that your eyes are being properly monitored for any risks.
Discuss Medication Risks:
If you’re taking medications that may increase the risk of retinal detachment, it’s important to discuss these risks with your doctor. Inform your healthcare provider about any concerns you have regarding the side effects of your medications. This can help ensure that you’re fully informed about potential risks, and your doctor can adjust your treatment plan if necessary to minimize those risks.
Additionally, your doctor may offer alternatives or monitor your eye health more closely while on certain medications. Always be open about any new medications you’re prescribed to stay proactive about your eye health.
Also Read: How to Recognize the Physical Symptoms of Anxiety
Avoid Eye Trauma:
Protecting your eyes from injury is crucial in reducing the risk of retinal detachment. When engaging in activities that could potentially lead to eye trauma, such as sports, construction work, or other hazardous tasks, wearing protective eyewear is highly recommended. Proper eye protection can prevent accidents that might destabilize the retina, decreasing the chances of a detached retina.
Consider using safety goggles, face shields, or other protective gear, especially if you’re involved in high-risk activities. Taking these precautions can help safeguard your vision for years to come.
Monitor Symptoms:
Being aware of sudden changes in your vision is key to identifying potential retinal issues early. Symptoms like flashes of light, floaters, or a shadow over your vision could indicate a retinal problem. If you experience any of these signs, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately to prevent further damage. Staying vigilant and promptly addressing changes in vision can make a significant difference in your eye health.
Keep track of any visual disturbances and communicate them with your doctor to ensure timely intervention. Early treatment can greatly reduce the risk of vision loss or permanent damage.
Additional Medications That May Increase Retinal Detachment Risk:
While fluoroquinolones, corticosteroids, and others are commonly discussed, several other medications have been linked to retinal detachment, albeit to a lesser extent. For example, certain antidepressants and antipsychotics may increase the risk of retinal issues, particularly in individuals with pre-existing eye conditions.
Medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and atypical antipsychotics might alter the retina’s structural integrity. Always consult with your doctor if you’re concerned about potential side effects and whether your medications may play a role in eye health.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Retinal Detachment Risk:
In addition to regular eye exams and medication management, lifestyle choices can play a significant role in protecting your vision. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins C and E, and omega-3 fatty acids can help support overall eye health.
Regular exercise, such as walking or swimming, can improve circulation and reduce the likelihood of conditions like high blood pressure, which may strain the blood vessels in the eyes. Avoiding smoking is another crucial factor, as smoking can increase the risk of retinal damage and worsen other eye health issues.
FAQ’s
- Which antibiotics can increase the risk of retinal detachment?
Fluoroquinolones, such as ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin, are linked to an increased risk of retinal detachment.
- Do corticosteroids contribute to retinal detachment?
Yes, corticosteroids like prednisone can lead to complications such as posterior vitreous detachment, which can precede retinal detachment.
- Is tamoxifen a risk factor for retinal detachment?
Yes, tamoxifen, often used for breast cancer, has been linked to retinal toxicity, increasing the risk of detachment.
- Can eye drops cause retinal detachment?
Epinephrine-based eye drops, used for glaucoma, can sometimes lead to retinal detachment, especially in susceptible individuals.
- Do thiazolidinediones (TZDs) increase retinal detachment risk?
Yes, medications like pioglitazone and rosiglitazone, used for type 2 diabetes, can contribute to fluid buildup in the eye, increasing the risk of retinal detachment.
Conclusion
While certain medications may increase the risk of retinal detachment, the overall likelihood remains low for most people. By understanding the potential risks and maintaining regular eye care, you can protect your vision and reduce the chances of complications. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or stopping any medication to ensure the benefits outweigh the risks.
Leave a Reply