Peripheral neuropathy can be a challenging condition for many individuals, especially those dealing with chronic pain. It encompasses a range of disorders that involve damage to the peripheral nervous system: the network of nerves connecting the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. Understanding what peripheral neuropathy entails, identifying its symptoms, and learning about treatment options are key to addressing this condition effectively.
What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of peripheral nerves, which play a central role in transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. The condition can result from various factors, including physical trauma and underlying health conditions. Peripheral neuropathy is not a single disease but rather a symptom or manifestation of an underlying issue. This serves as a key distinction, as addressing the root cause is often pivotal in managing the condition. Common causes include diabetes, infections, and hereditary conditions.
What Are the Symptoms?
The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy vary widely depending on the type of nerves affected: sensory, motor, or autonomic. This can affect the extent of the damage. Some common manifestations across these categories are organized below.
Sensory Symptoms
Sensory nerves play a role in feeling or sensing stimulation and pain. Tingling sensations or burning feelings are a common symptom of sensory nerve damage. Numbness or reduced ability to feel pain, temperature, or touch can be a factor as well.
Motor Symptoms
Motor nerves affect muscle movement. Muscle weakness, leading to reduced coordination and difficulty performing fine motor tasks can be a result of motor nerve damage. Paralysis may occur in severe cases, where nerve damage impairs the ability to move specific body parts.
Autonomic Symptoms
Autonomic nerves are central to internal bodily functions. Digestive troubles, including bloating, constipation, or diarrhea may occur. Heart rate changes and episodes of dizziness or fainting due to low blood pressure are another possible symptom.
How is It Treated?
While peripheral neuropathy cannot always be reversed, various strategies may focus on managing symptoms and limiting further nerve damage. Treatment plans are typically tailored to address the specific cause of the condition while alleviating discomfort and improving quality of life.
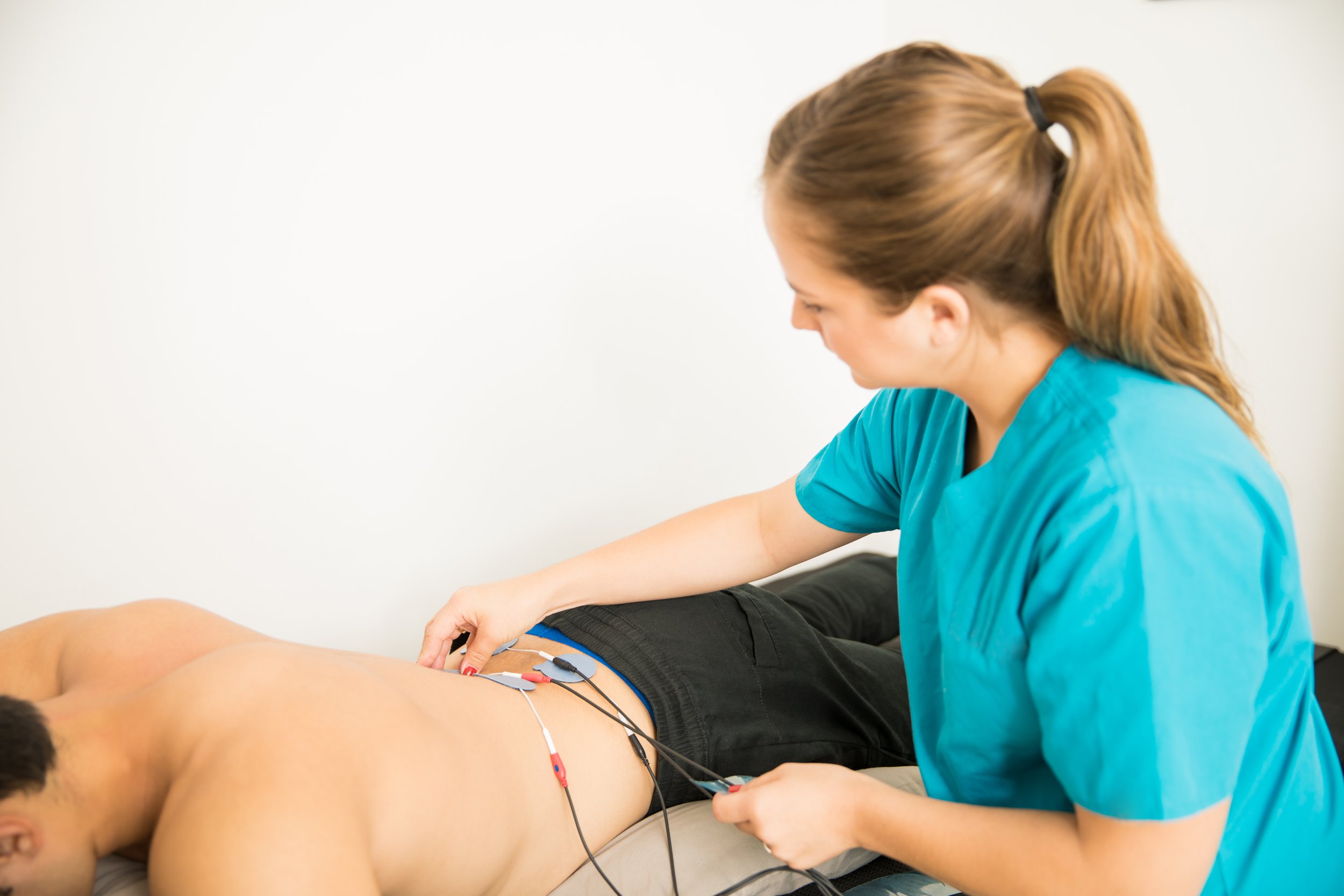
Medications and Therapies
Several medications are used to manage symptoms, including over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription drugs, and topical treatments. Physicians may recommend nerve blocks, depending on the severity of the symptoms. Physical and occupational therapy can also help maintain muscle strength, improve coordination, and develop strategies to accomplish daily tasks more easily.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Adopting healthy habits may play an integral role in managing peripheral neuropathy symptoms. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding alcohol products can contribute positively to overall nerve health. Facilitating proper foot care is particularly of interest to those experiencing symptoms in the lower extremities, as reduced sensation increases the risk of injuries and infections.
When to Seek Medical Care
Peripheral neuropathy can significantly affect the day-to-day lives of those living with chronic pain. If you notice persistent tingling, numbness, or weakness, reaching out to a healthcare provider is recommended. Early intervention may help minimize long-term damage and identify the underlying cause, potentially improving outcomes and quality of life.
- What Is Medicaid Exclusion For Funeral Plans – Benefits of Medicaid Funeral Exclusions!
- Banner Desert Medical Center – Trusted Care in Arizona!
- Why Cranberry Femine Health – The Ultimate Natural Wellness Guide for Women!
- What Is The Best Peptide For Bone Health – A Comprehensive Overview!
- Why Is Signify Health Calling Me – Understanding the Purpose Behind the Call!
Leave a Reply